Juices vs. Fruits vs. Vegetables: The Ultimate Nutrition Showdown

When it comes to getting essential nutrients into our diet, we’re often faced with choices: Should I drink that fresh orange juice, eat the whole orange, or perhaps reach for some leafy greens instead? Each option offers unique benefits, but understanding their differences can help you make the best choice for your health goals.
The Juice Dilemma

When Convenience Meets Nutrition Loss
Fresh juices can be a quick way to consume multiple servings of fruits and vegetables, but they come with significant trade-offs.
The Downsides:
- Fiber removal: Most juicing processes remove the beneficial fiber found in whole produce
- Concentrated sugars: Even natural fruit sugars become problematic when consumed in large quantities without fiber to slow absorption
- Calorie density: It’s easy to consume 3-4 servings worth of fruit calories in a single glass
- Oxidation: Nutrients begin breaking down immediately after juicing, especially when exposed to air and light
The Case for Whole Fruits
Why Fruits Win Points for Fiber
Whole fruits are nutritional powerhouses that come perfectly packaged by nature. When you bite into an apple or orange, you’re getting not just vitamins and minerals, but also crucial dietary fiber that’s often lost in processing.
Key Benefits:
The Vegetable Advantage
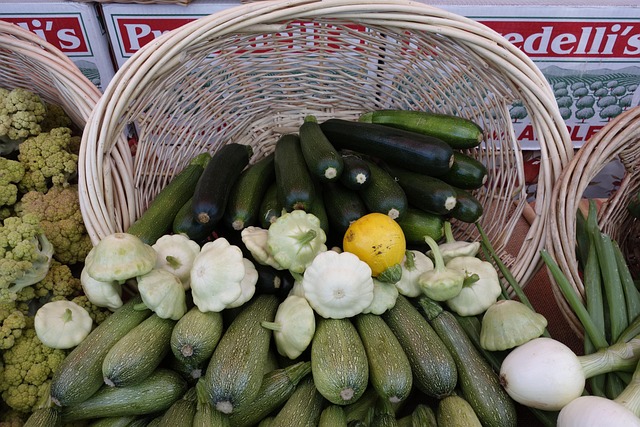

Nutrient Density Without the Sugar
Vegetables often edge out fruits in the nutrition department, offering more vitamins and minerals per calorie while containing significantly less natural sugar.
Why Vegetables Take the Lead:
- Lower glycemic impact: Most vegetables have minimal effect on blood sugar levels
- Higher nutrient density: Leafy greens like spinach and kale pack more vitamins A, K, and folate per serving than most fruits
- Versatility: Can be eaten raw, cooked, or blended without major nutrient loss
- Anti-inflammatory compounds: Many vegetables contain unique phytonutrients that help reduce inflammation
Vegetable Superstars
Dark leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts, and colorful bell peppers offer some of the highest concentrations of essential nutrients with minimal calories.
The Verdict: What’s Actually Better?
For Overall Health: Whole Fruits and Vegetables Win
The scientific consensus heavily favors whole produce over juice. The combination of fiber, nutrients, and natural portion control makes whole fruits and vegetables the superior choice for most people.
When Each Option Makes Sense
Choose Whole Fruits When:
- You want a natural sweet treat
- You need sustained energy
- You’re trying to manage weight
- You want to improve digestive health
Choose Vegetables When:
- You’re focused on maximizing nutrients while minimizing calories
- You want to reduce sugar intake
- You’re managing blood sugar levels
- You need specific nutrients like iron, folate, or vitamin K
Consider Fresh Juice When:
- You’re recovering from illness and need easily digestible nutrients
- You struggle to eat enough produce in whole form
- You want a quick nutrient boost before or after intense exercise
- You’re using it as an occasional supplement, not a replacement
Making the Best Choice for You
Rather than viewing this as an either/or decision, consider your individual health goals, lifestyle, and preferences. The best approach for most people combines all three:
- Base your diet on whole fruits and vegetables
- Use fresh juice sparingly as a supplement or treat
- Focus on variety to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients

Practical Tips
- If you do juice, drink it immediately and consider adding back some fiber with chia seeds or ground flaxseed
- Aim for more vegetables than fruits in your daily intake
- When choosing juice, opt for vegetable-based options with minimal fruit added
- Remember that frozen fruits and vegetables can be just as nutritious as fresh ones
The Bottom Line
While fresh juices have their place, whole fruits and vegetables consistently come out on top for overall health benefits. The fiber, natural portion control, and complete nutrient profiles of whole produce make them the clear winners. Vegetables slightly edge out fruits due to their lower sugar content and higher nutrient density, but both whole fruits and vegetables are excellent choices that should form the foundation of a healthy diet.
3 Comments